What is a Relay Switch? Is it the Same As a Relay?
What is a Relay Switch?
A relay switch is an electronic device that controls the flow of electricity from one circuit to another. This device is commonly used for radio and television signals, as well as high-current circuits for motors, lamps, and other items. It is often used in situations when the existing circuit cannot handle the amount of current needed.
A relay switch has two spring contacts and an electromagnet coil inside. A pulse to one coil turns the relay on and a pulse to the other coil turns it off. It is used in avionics, as well as numerous industrial applications.
Relays are typically made of copper, aluminum, or other low-density alloy. The coils in a relay contain a small amount of resistance. This resistance determines the amount of power a relay consumes. As a result, it is best to select materials with lower resistance in order to keep the relay under safe operating conditions.
What is a Relay Switch? Is it the Same As a Relay?
Relays can be electromechanical or solid state devices. A typical electromechanical relay is made with a copper coil wound on a metal core. The two ends of the coil are connected to two pins in a relay switch. The other two contacts, called “switching points,” are connected to a high-amperage load. These switching points are also connected to a common contact.
Relays are also used to control inductive loads. Relays are often required to specify the maximum current they can handle when activated. This is known as the make rating. This rating can be several times higher than the break rating. This is because inductive loads can be sensitive to external factors. A solid state relay can withstand a high-powered electrical environment.
There are many types of relays. Different types have different functions. Some can be used in non-relay applications while others are designed for high-amperage signals. The right choice is essential for the reliability and integrity of the switched signal. When choosing the right relay, you should consider other factors, such as the size, operating temperature, and the coil voltage and current.
Relays have two basic functions: they switch electrical current through one circuit while breaking another circuit. Relays can have up to 12 separate terminals, called poles. Single-pole contacts are able to control one circuit at a time, while double-pole contacts can handle two circuits.
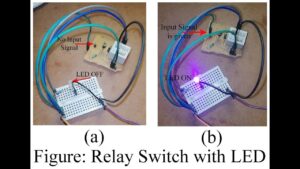
A typical relay switch circuit consists of a TR1 or NPN transistor. The collector current of TR1 turns on the switching transistor TR2. A small resistor is placed between the Base and the Emitter of the main switching transistor. The collector current drives the coil of the relay.
Reed relays contain a reed switch and are enclosed in a solenoid. A glass tube filled with an inert gas protects the contacts from atmospheric corrosion. Reed relays can switch industrial components.